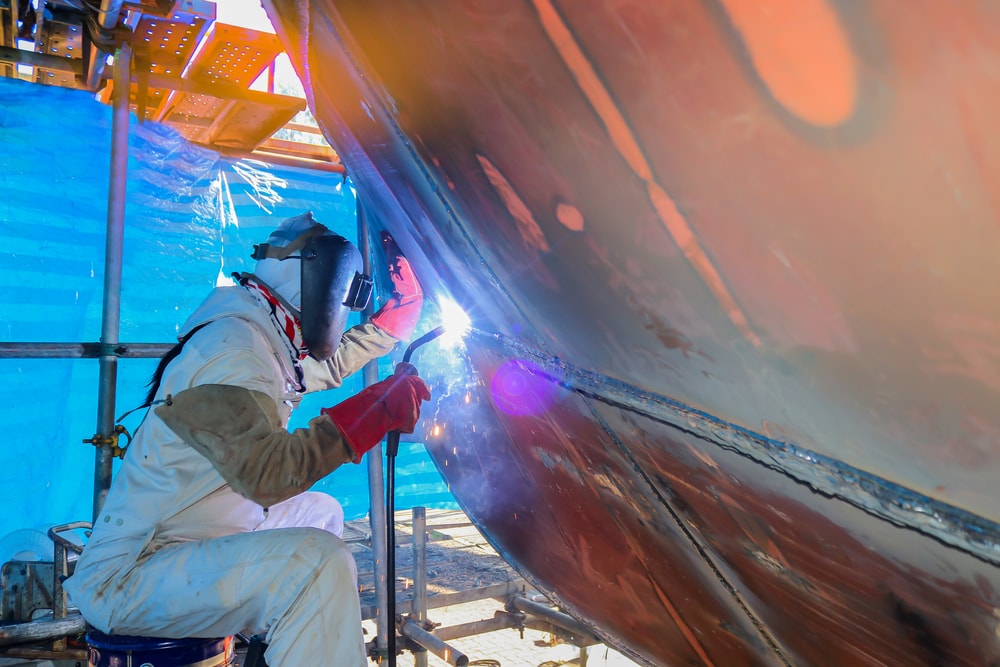
Marine welding, as the name suggests, is the welding process specifically tailored for marine applications and structures, primarily in shipbuilding, offshore construction, and marine repairs. While it shares similarities with other welding techniques, there are several key differences that set marine welding apart:
1. Corrosion Resistance: Marine welding focuses heavily on the use of materials with exceptional corrosion resistance, especially when dealing with saltwater environments. Stainless steel and aluminum are commonly preferred materials due to their ability to withstand corrosion caused by exposure to seawater.
2. Stricter Standards: Marine welding adheres to more stringent standards and regulations compared to some other welding applications. The welding must meet specific marine classification society standards (e.g., American Bureau of Shipping – ABS, Det Norske Veritas – DNV) to ensure the structural integrity and safety of marine vessels and offshore structures.
3. Water Tightness: In marine welding, special attention is given to achieving water-tight joints, as the welded structures must withstand the constant exposure to water and pressure variations. Proper welding techniques, like full penetration welds, are employed to create durable and watertight connections.
4. Environmental Considerations: Marine welding takes into account the harsh environmental conditions present at sea, including high humidity, temperature variations, and constant exposure to saltwater. Proper welding procedures and materials are chosen to withstand these challenges and prevent premature deterioration.
5. Welding Positions: Marine welding often requires welding in challenging positions, such as overhead and vertical positions, especially during ship construction and repair. Welders need to be skilled and experienced in handling such positions effectively.
6. Diverse Applications: Marine welding encompasses a wide range of applications, from building massive ship hulls and offshore platforms to smaller components like handrails, brackets, and equipment installations. Each application may require different welding techniques and approaches.
7. Inspection and Quality Assurance: Due to the critical nature of marine structures and their potential impact on human lives, thorough inspection and quality assurance are integral parts of marine welding projects. Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods like ultrasound and radiography are commonly employed to ensure weld integrity.
8. Remote Locations: Marine welding often takes place in remote locations, such as offshore oil rigs or remote shipyards. This can present logistical challenges, requiring welders to have adaptability and the ability to work in diverse conditions.
In summary, marine welding differs from other welding applications due to its focus on corrosion resistance, adherence to strict standards, emphasis on water-tightness, consideration of environmental factors, and the need for welding in challenging positions. It plays a crucial role in building and maintaining safe and reliable marine structures that withstand the harsh conditions of the open sea.